Segy-change
Segy-change (https://gitlab.com/giuseppe.stanghellini/segy-change)
Data collected during seismic reflection surveys can be stored in many different, more or less standard, formats.
One of the most popular is the SEGY format, developed since 1975 to store single-line seismic digital data on tapes and now evolved to store them into hard-disk and other media as well.
Here we present segy-change, a software program to manipulate SEG-Y data files.
It is written in the ”C” programming language, can be used also as a software library and is compatible with most operating systems. The software allows the user to display and optionally change the values inside all parts of a SEG-Y file: the file header, the trace headers and the data blocks.
In addition, it allows to do a quality check on the data by plotting the traces.
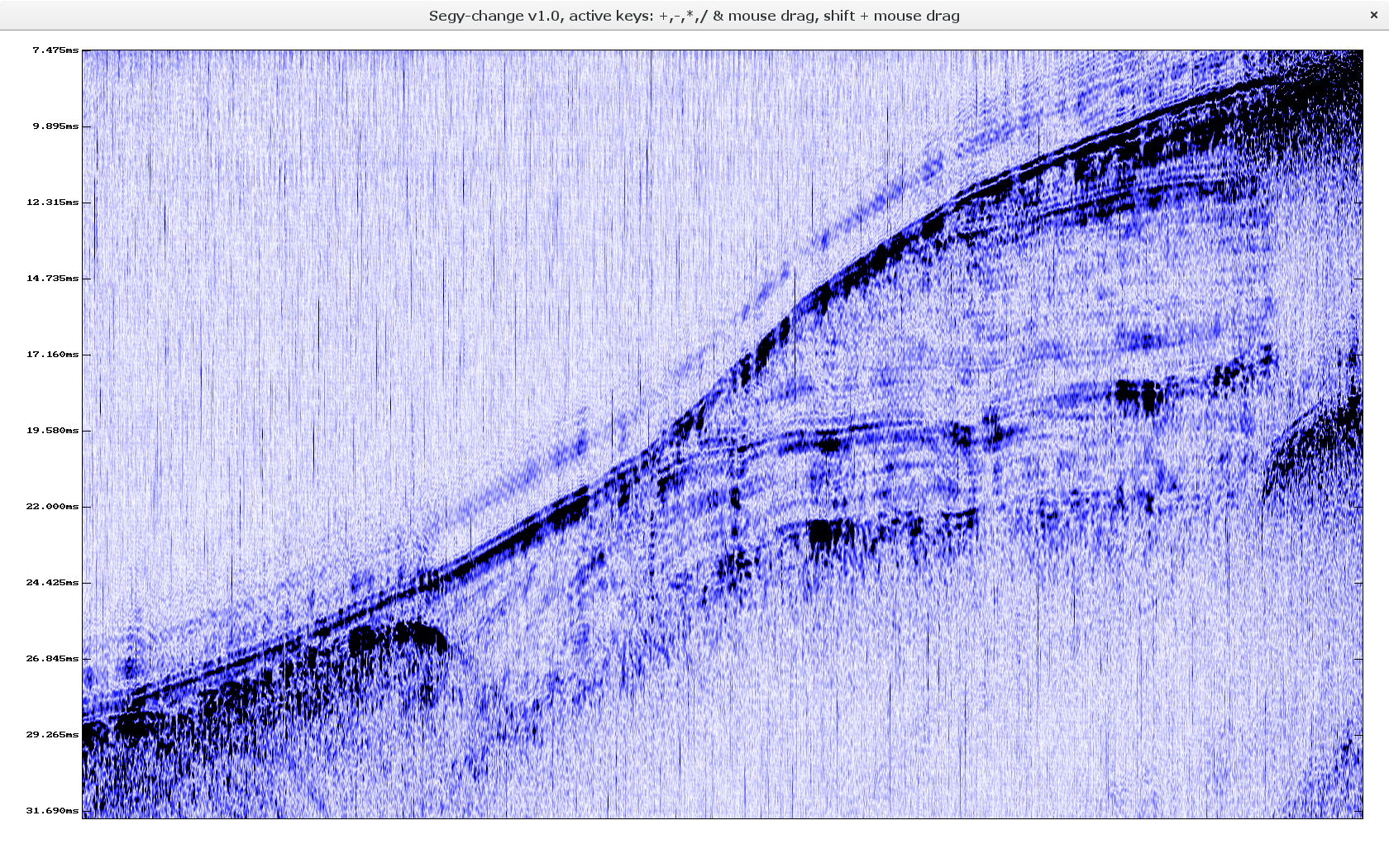
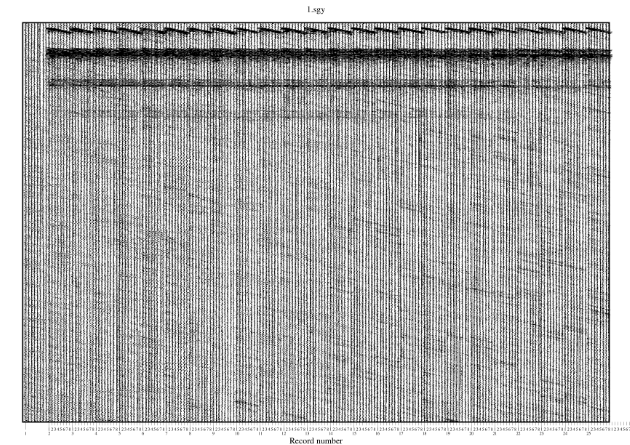
The software segy-change can be downloaded from gitlab: https://gitlab.com/giuseppe.stanghellini/segy-change
The manual page of the program is printed out by the use of the switch -h on the command line:
segy-change -h
segy-change: a progam to read and optionally change
the contents of segy seismic data files.
If you use this software for scientific publication, please cite:
G. Stanghellini, G. Carrara
Segy-change: The swiss army knife for the SEG-Y files
SoftwareX, Volume 6, 2017, Pages 42–47, DOI:10.1016/j.softx.2017.01.003
Copyright (C) 2016, Giuseppe Stanghellini (1), Gabriela Carrara (2).
(1) Istituto di Scienze Marine, Geologia Marina, CNR, Bologna, Italy
(2) Independent Researcher, Monte San Pietro, Italy
This program comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY! see GPLV3.
This is free software, and you are welcome to redistribute it
under certain conditions; for details see the GPLV3 license
as published in 'http://www.gnu.org/licenses/'
Usage : segy-change [options] -f input_file [-o output_file]
Input & output:
-f input_file : The input file (use "-" for stdin)
-o output_file : The output file (use "-" for stdout)
Switches:
-flip_endianess : Flip endianess, useful to make
the file conformant to SEGY standard.
-change_header_fields : Change SEGY header fields given an offset,
Use the following syntax:
offset0:type0:value0,...
where type can be S for short (2 bytes) or
I for int (4 bytes)
or
parameter0_name:value,parameter1_name:value,...
To know at which offsets a field is stored
or which parameters are available, use the
'-segy_info and -use_names switches.'
-change_trace_fields : Change trace header fields given a file with values.
The file must be in the same format as the output
obtained by the -dump_trace_fields switch,
with or without the -use_names switch.
-dump_xy : Print x and y location to stdout.
SOURCE|RECEIVER the word SOURCE or RECEIVER must be given, according
to locations to print.
-vertical_stack num : Do a vertical stack, summing num samples together
-add_xy : Add coordinates (in m, feet or arcsec) to trace
fname,SOURCE|RECEIVER header, given a filename and one of the two words
SOURCE or RECEIVER, depending on whose entries of the
trace headers we want to update.
The specified file must contain for each line:
the original_field_record_number,
the trace_sequence_number_within_reel,
the trace_number_within_field_record,
the x coordinate,
the y coordinate,
the z elevation,
the unit of measure,
ie:
1 1 1 3600 4500 100 meters
2 1 1 3602 4400 101 arcsec
2 1 2 3602 4400 103 meters
5 1 1 3608 4200 105 meters
...
NOTE: to have the lines with the first three numbers
of a given file, execute:
segy-change -print_rec_seq_num -f segyfile
you can then just add coordinates and the unit of
measure in the proper format for each line.
-do_op +|-|*|/:VAL : Do the given operation, for example to multiply all
trace values by 3.0 use: -do_op *:3.0
-debias : Subtract from each trace (MAXVAL+MINVAL)/2
-convert S|I|F|E : Convert the trace encoding to the given format, where
S: short
I: integer
F: IBM floating point
E: IEEE 754.
-do_ps siz,n,sc : Plot the segy to a postscript file where:
siz = paper size (for example A4)
n = number of traces per cm to plot
sc = factor to multiply trace values, darkening
(if>1) or lightening (if<1) the plot.
Valid paper sizes are: A0,A1,A2,A3,A4.
-print_rec_seq_num : Print to stdout the original_field_record_number,
trace_sequence_within_line and
trace_sequence_within_field_record terna.
-scan : Scan SEGY and print some info.
-dump : Dump traces values to stdout.
-dump_header_fields : Dump header fields stored into the traces header.
Use it with the following syntax:
field_offset0:field_type0,offset1:type1,...
where type can be S for short (2 bytes) or
I for int (4 bytes)
or
parameter0_name,parameter1_name,...
To know at which offsets a field is stored
or which parameters are available, use the
'-segy_info and -use_names switches.'
-dump_trace_fields : Dump fields from trace header given an offset,
syntax is field_offset0:field_type0,...
where type can be S for short (2 bytes),
I for int (4 bytes)
or
parameter0_name,parameter1_name,...
To know at which offsets a field is stored
or which parameters are available, use the
'-segy_info and -use_names switches.'
-only_traces_with : Keep only traces with fields from trace header
with a given value
syntax is field_offset0:field_type0:value,...
where type can be S for short (2 bytes),
I for int (4 bytes)
or
parameter0_name:value,parameter1_name:value,...
To know at which offsets a field is stored
or which parameters are available, use the
'-segy_info and -use_names switches.'
-use_names : use names instead of offsets.
to have a list of available parameters names use:
segy-change -segy_info -use_names
-info : Write the SEGY header and exits.
-EBCDIC file : Replace the EBCDIC header section with the content
of the specified ASCII file, converting it to EBCDIC
-irc num : Do a record renumbering starting from num.
-itc num : Do a trace renumbering starting from num.
-no_header : Do not write the SEGY header into the output file.
Useful to concatenate SEGY files or to make a file
in SU format to be processed with Seismic Unix.
-segy_info : Write the SEGY header formats and exits.
-record num num : The record interval to process. Tested against
the 'Original_field_record_number' field
-trace num num : Set the trace interval to process. Tested against
the 'Trace_number_within_field_record' field.
-only_n_traces num : Consider the file long at most 'num' traces.
-skip_n_traces num : Skip the first 'num' traces.
-only_n_samples num : Consider the trace only long at most 'num' samples.
-skip_n_samples num : Skip the first 'num' samples.
-num_trace_offset num : Set the offset at which, into the trace header,
there is the field to use for the trace number.
Useful when we don't want to use the
'Trace_number_within_field_record' field.
-traces_per_record num: If the traces per record value stored into the segy
header is wrong you can use this to override it.
Please note that in this way you do not change the
actual value inside the header, to do this you must
use -change_header_fields switch.
-samples_per_trace : If the samples per trace value stored into the traces
header is wrong you can use this to override it.
Please note that in this way you do not change the
actual value inside the header, to do this you must
use -change_trace_fields switch.
-v num : Verbosity level: 1 | 2 | 3
-x num : Skip num bytes at the beginning of input file.
-view : Display segy data.
Examples:
- To convert a whole file to a 4-byte ibm floating point format:
segy-change -f in.segy -o out.segy -convert F
- To change the value of 'Number of samples per data trace for this reel'
into the segy header:
segy-change -f in.segy -o out.segy -change_header_fields 3220:S:3000
- To dump some trace fields from all the trace headers:
segy-change -f in.sgy -dump_trace_fields 0:I,8:I
- To change the 'Traces per record field' into the segy header:
segy-change -f in.sgy -o out.sgy -change_header_fields 3212:S:4000
-traces_per_record 4000
- To extract traces containing exactly 10000 samples:
segy-change -f in.segy -o out.segy -use_names
-only_traces_with NUMBER_OF_SAMPLES_IN_THIS_TRACE:10000
- To make a postscript plot of the first two shot-gather, with 25 traces
per cm:
segy-change -f in.segy -record 100 101 -trace 1 120
-do_ps A4,25,0.01
- To view interactively the segy:
segy-change -f in.segy -view
For your information this machine is LITTLE_ENDIAN and the size of int appears
to be 4 bytes, as it should be.
***********************************************************************
If you use this software for scientific publication, please cite:
G. Stanghellini, G. Carrara
Segy-change: The swiss army knife for the SEG-Y files
SoftwareX, Volume 6, 2017, Pages 42–47, DOI:10.1016/j.softx.2017.01.003
***********************************************************************